Build-Measure-Learn: The Lean Startup Methodology Masterclass
The Lean Startup methodology has revolutionized the way businesses approach product development and market entry. At its core, the Build-Measure-Learn cycle offers a systematic approach to creating products that truly resonate with customers while minimizing waste and maximizing learning. This article delves deep into the principles of Lean Startup, exploring how this methodology can be applied to accelerate innovation, reduce risk, and achieve product-market fit more efficiently. We'll examine each component of the Build-Measure-Learn cycle, discuss the importance of Minimum Viable Products (MVPs), and provide practical insights on implementing these strategies in your business.
Discover molfar.io
At molfar.io, we specialize in turning innovative ideas into market-ready products using the Lean Startup methodology. Our approach to MVP development for startups is designed to help you navigate the uncertain waters of product development with confidence. By leveraging our expertise in custom software development and IT consulting, we guide you through each stage of the Build-Measure-Learn cycle, ensuring that your product evolves based on real market feedback. Whether you're a startup founder or an established business looking to innovate, our team can help you apply Lean Startup principles to create products that truly meet market needs and drive business growth.
Understanding the Lean Startup Methodology
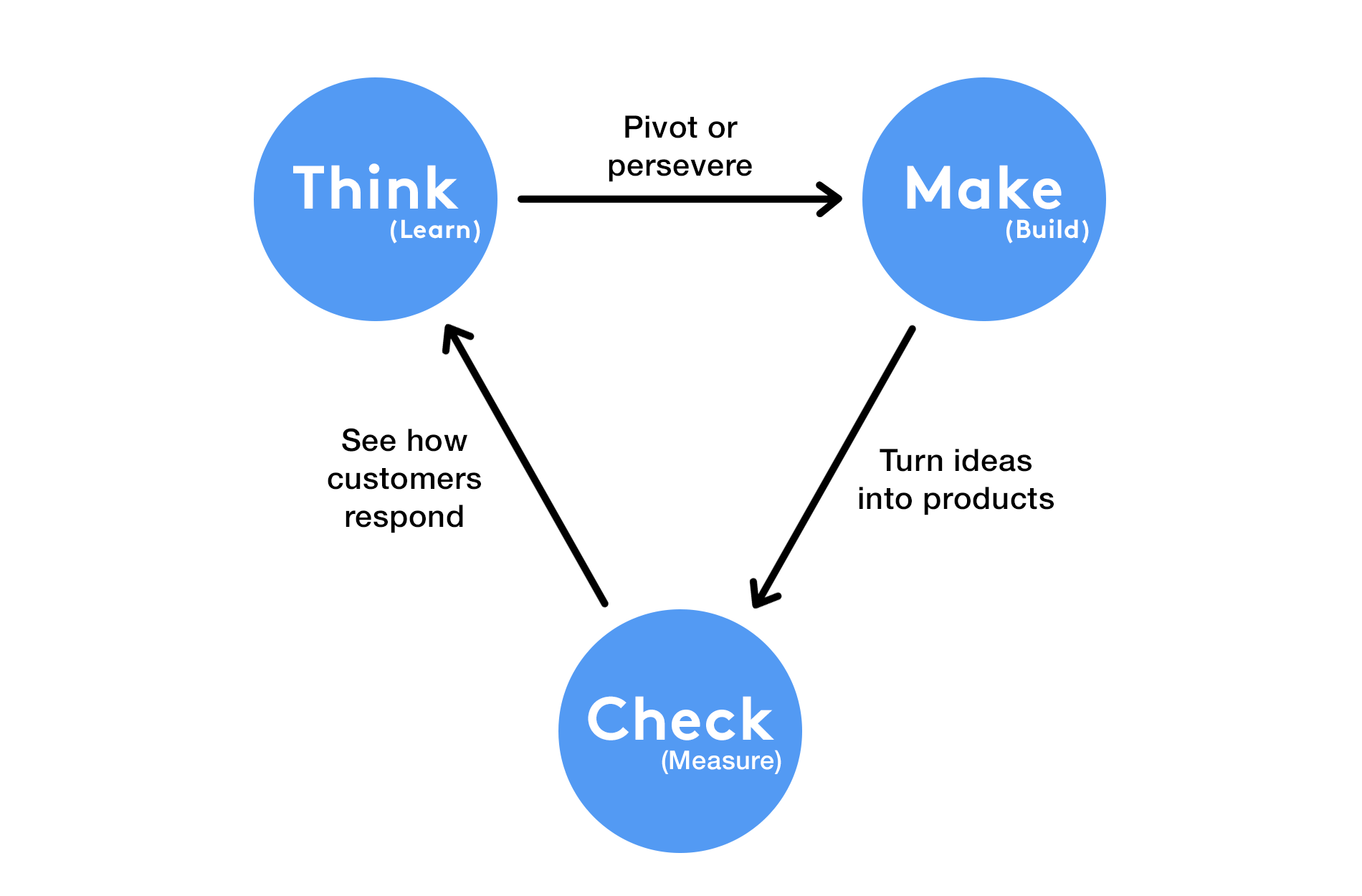
The Lean Startup methodology, popularized by Eric Ries, is a scientific approach to creating and managing startups and getting desired products to customers' hands faster. It teaches you how to drive a startup - how to steer, when to turn, and when to persevere - and grow a business with maximum acceleration. At its heart is the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop, a core component that drives the development process.
The Build-Measure-Learn Cycle Explained
The Build-Measure-Learn cycle is the fundamental activity of a Lean Startup. It's a systematic process that allows startups to test their vision continuously, adapting and adjusting before wasting time and resources on building products that customers don't want. Let's break down each component:
Build: This phase involves creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that tests a fundamental business hypothesis. The MVP is not about creating a minimal product, but about the fastest way to get through the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop with the least amount of effort.
Measure: Once the MVP is built, the focus shifts to measuring how customers respond. This involves setting up the right metrics and analyzing the data to understand user behavior and product performance.
Learn: The data collected in the Measure phase is then used to learn and make informed decisions. This learning helps in validating or invalidating the initial hypothesis and guides the next steps in product development.
This cycle is iterative, meaning it's repeated multiple times throughout the product development process, each time refining the product based on what has been learned.
The Role of MVPs in Lean Startup
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a core concept in the Lean Startup methodology. It's the version of a new product that allows a team to collect the maximum amount of validated learning about customers with the least effort. The key aspects of an MVP include:
Focused functionality: An MVP includes only the core features necessary to solve the primary problem for your target users, allowing for faster development and deployment.
Rapid iteration: The goal is to get the product into users' hands quickly, gather feedback, and iterate based on that feedback.
Learning orientation: The primary purpose of an MVP is to learn about the market and validate assumptions, not to generate revenue or gain market share immediately.
At molfar.io, we specialize in developing MVPs that strike the right balance between functionality and speed to market. Our approach ensures that you can start gathering valuable user feedback as quickly as possible, setting the foundation for data-driven product evolution.
Implementing the Build Phase
The Build phase is where ideas start to take tangible form. It's crucial to approach this phase with a clear strategy to ensure that you're building something that can effectively test your hypotheses without overcommitting resources. Here's how to implement the Build phase effectively:
Defining Your MVP
Before you start building, it's essential to clearly define what your MVP will look like. This involves:
Identifying core features: Determine the minimum set of features that will allow you to test your primary value proposition. Focus on what's essential for solving your users' key problem.
Setting clear hypotheses: Each feature or aspect of your MVP should be tied to a specific hypothesis you want to test. This ensures that every part of your MVP serves a purpose in your learning process.
Outlining success criteria: Define what success looks like for your MVP. This could be in terms of user engagement, sign-ups, or other relevant metrics that will help you validate your hypotheses.
At molfar.io, we work closely with our clients to define MVPs that are lean yet powerful enough to provide meaningful insights. Our experience across various industries allows us to help you focus on the features that will give you the most valuable learnings.
Rapid Prototyping Techniques
Rapid prototyping is a crucial skill in the Lean Startup toolkit. It allows you to create a working model of your product quickly, which can be used for internal testing, stakeholder presentations, and even early user feedback. Some effective rapid prototyping techniques include:
Paper prototyping: Sketching out user interfaces and workflows on paper. This is incredibly fast and allows for quick iterations in the early stages of design.
Digital wireframing: Using tools like Figma or Sketch to create more detailed, interactive mockups of your product.
No-code platforms: Utilizing platforms that allow you to build functional prototypes without extensive coding, which can be especially useful for testing user flows and basic functionalities.
Our team at molfar.io is adept at various rapid prototyping techniques, helping you move from concept to testable prototype in record time. This approach allows us to validate ideas quickly and adjust based on early feedback, saving time and resources in the long run.
Agile Development for MVPs
Agile methodologies align perfectly with the Lean Startup approach, especially when it comes to building MVPs. Key principles of Agile development that are particularly relevant include:
Iterative development: Breaking the development process into small, manageable sprints, typically 1-2 weeks long.
Continuous integration and delivery: Regularly integrating new code and deploying updates to ensure the product is always in a releasable state.
Cross-functional teams: Bringing together developers, designers, and business stakeholders to ensure all perspectives are considered throughout the development process.
At molfar.io, we employ Agile methodologies in our MVP development process, ensuring that we can pivot quickly based on new learnings and deliver value to our clients faster. This approach allows us to maintain flexibility while still adhering to project timelines and budgets.
Mastering the Measure Phase
The Measure phase is critical in the Lean Startup methodology as it provides the data necessary to make informed decisions about product development. Effective measurement allows you to understand how users interact with your MVP and whether your initial hypotheses were correct. Here's how to excel in the Measure phase:
Selecting the Right Metrics
Choosing the appropriate metrics is crucial for gaining meaningful insights. It's important to focus on actionable metrics that directly relate to your business goals and hypotheses. Some key considerations when selecting metrics include:
Relevance to your business model: Ensure that the metrics you choose align with your overall business objectives and can inform critical decisions.
Specificity: Opt for metrics that provide clear, specific insights rather than vanity metrics that might look impressive but offer little actionable information.
Measurability: Select metrics that can be accurately measured with the tools and resources at your disposal.
At molfar.io, we work with our clients to identify the most relevant metrics for their unique situation, ensuring that the data collected will drive meaningful product improvements and business decisions.
Implementing Analytics Tools
To effectively measure user behavior and product performance, you need the right tools in place. Some essential analytics tools and techniques include:
Web analytics: Tools like Google Analytics or Mixpanel can provide insights into user behavior, traffic sources, and engagement metrics.
User session recording: Tools such as Hotjar or FullStory allow you to see how users interact with your product, identifying pain points and areas for improvement.
A/B testing platforms: Platforms like Optimizely or VWO enable you to test different versions of your product to see which performs better.
Our team at molfar.io has extensive experience in implementing and configuring these tools to ensure you're capturing the most relevant data for your MVP. We can help you set up a comprehensive analytics infrastructure that provides real-time insights into your product's performance.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data
A balanced approach to data collection, incorporating both qualitative and quantitative data, provides the most comprehensive understanding of your MVP's performance. Here's how to leverage both types of data:
Quantitative data: Numerical data that can be measured and analyzed statistically. This includes metrics like user acquisition costs, conversion rates, and engagement times.
Qualitative data: Non-numerical data that provides insights into user motivations, preferences, and pain points. This can be gathered through user interviews, surveys, and feedback sessions.
At molfar.io, we employ a mixed-methods approach to data collection, ensuring that our clients have both the hard numbers and the contextual insights needed to make informed decisions about their product development.
Maximizing the Learn Phase
The Learn phase is where the insights gathered during the Measure phase are transformed into actionable knowledge. This is the stage where you validate or invalidate your initial hypotheses and make critical decisions about the future direction of your product. Here's how to make the most of the Learn phase:
Interpreting Data and Drawing Conclusions
Effective data interpretation is crucial for deriving meaningful insights from your measurements. This process involves:
Pattern recognition: Identifying trends and patterns in your data that might indicate user preferences or pain points.
Hypothesis validation: Determining whether the data supports or refutes your initial assumptions about your product and market.
Contextual analysis: Considering external factors that might influence your data, such as market conditions or seasonal trends.
At molfar.io, our data analysts work closely with our clients to interpret the collected data, ensuring that all insights are contextualized within the broader business strategy and market environment.
Decision Making: Pivot or Persevere
One of the most critical decisions in the Lean Startup process is whether to pivot or persevere based on the learnings from your MVP. This decision involves:
Evaluating progress: Assessing whether your current strategy is moving you closer to your business goals at an acceptable pace.
Identifying pivot opportunities: If the current approach isn't working, consider potential pivots that could better address market needs or capitalize on unexpected opportunities.
Assessing resource implications: Understanding the resource requirements and potential risks associated with pivoting versus persevering.
Our team at molfar.io has extensive experience guiding startups through these critical decision points, helping to analyze the data objectively and make informed choices about product direction.
Iterating and Refining Your MVP
Based on the learnings from your data analysis, the next step is to refine your MVP. This iterative process involves:
Prioritizing changes: Identifying the most impactful improvements based on user feedback and data insights.
Rapid implementation: Quickly implementing changes to test new hypotheses or address identified issues.
Continuous learning: Maintaining an ongoing cycle of building, measuring, and learning to continually refine your product.
At molfar.io, we specialize in agile development practices that allow for rapid iteration and refinement of MVPs. Our approach ensures that each iteration brings your product closer to achieving product-market fit.
Conclusion
The Lean Startup methodology, centered around the Build-Measure-Learn cycle, offers a powerful framework for developing products that truly meet market needs while minimizing waste and maximizing learning. By embracing this approach, startups and established businesses alike can navigate the uncertain waters of product development with greater confidence and efficiency.
Key takeaways from this masterclass include:
The importance of starting with a well-defined MVP that tests core business hypotheses.
The need for robust measurement systems to gather meaningful data about your product's performance.
The critical role of data interpretation and learning in guiding product development decisions.
The value of an iterative approach that allows for rapid adaptation based on market feedback.
At molfar.io, we're committed to helping businesses implement the Lean Startup methodology effectively. Our expertise in MVP development, data analytics, and agile methodologies positions us uniquely to guide you through each stage of the Build-Measure-Learn cycle.
Ready to apply these principles to your next project? Contact us today to learn how we can help you develop market-aligned products faster and more efficiently using the Lean Startup approach. Let's work together to turn your innovative ideas into successful products!